CogAT Nonverbal assesses visual and spatial reasoning skills, making it an essential part of the Cognitive Abilities Test.
This guide provides clear strategies, sample questions, and simple activities to boost your child’s nonverbal reasoning abilities.
Whether your child is new to this type of question or needs extra practice, these tips will make preparation easier and more effective.
By following the steps outlined here, you can help your child approach the test with confidence and perform at their best.
Let’s dive into the tools and techniques that will support their success!

Hey there! Do you have a question about the test or our practice package? Email me at roman@staggingapps.website. I'm here to help your child succeed!
The Nonverbal section of CogAT evaluates a child’s visual and spatial reasoning skills through tasks such as figure matrices, paper folding, and shape classification. Since it does not rely on language, it provides a fair assessment of cognitive abilities, especially for children who may face language challenges.
These skills are critical for problem-solving in areas like math and science. They also improve pattern recognition and critical thinking, which are valuable for academic and everyday problem-solving.
This section is particularly beneficial for children learning English or those with language-related difficulties, as it emphasizes visual-spatial reasoning over verbal comprehension.
This section includes three types of questions that measure a child’s ability to identify patterns and relationships between shapes: Figure Matrices, Paper Folding, and Figure Classification.
Each type focuses on a unique aspect of spatial reasoning and problem-solving, providing a comprehensive evaluation of these critical skills.
Figure Matrices present a 2×2 grid with three visible shapes and one empty space. Children must identify the relationship between the shapes in the top row. Then, they must apply that pattern to complete the bottom row by selecting the correct answer from the options provided.
These questions emphasize logical thinking and the ability to recognize patterns, helping assess a child’s reasoning skills.
Sample Question:
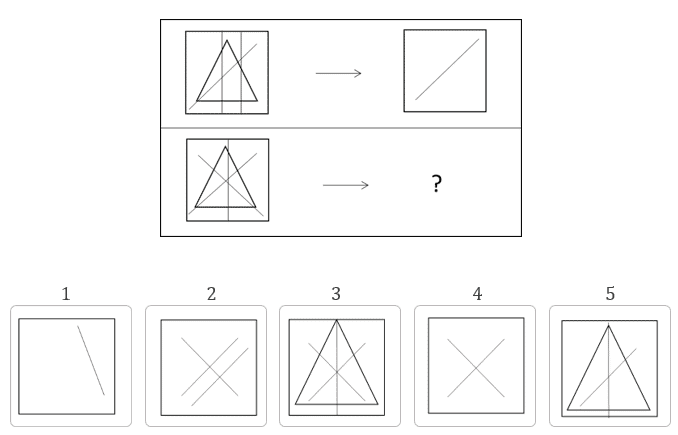
The correct answer is 4.
In the top row, the left frame contains a triangle, a diagonal line, and two vertical lines. The right frame contains only the diagonal line.
The same relationship will hold for the bottom row.
The answer choice will contain only the two diagonal lines present in the bottom-left frame.
Therefore, answer choice 4 is the correct answer.
Paper Folding questions show a series of diagrams where a piece of paper is folded, and a hole is punched or cut. The child’s task is to predict how the paper will appear when unfolded, taking into account how the holes reflect across the folds.
Sample Question
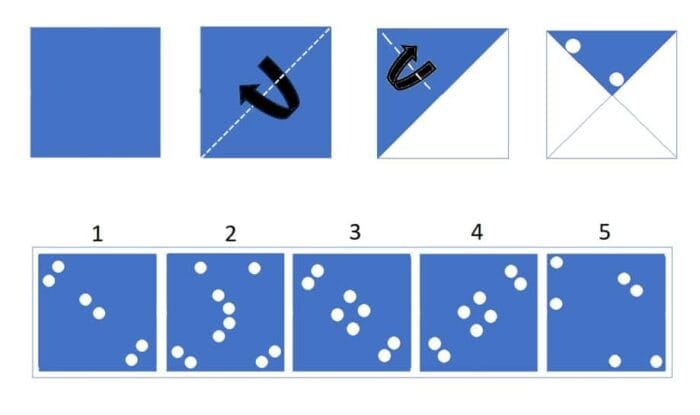
The correct answer is 3.
Hence, the correct answer is 3.
Incorporating simple, everyday activities into your child’s routine is a highly effective way to enhance their nonverbal reasoning skills. These activities not only make learning enjoyable but also provide opportunities to practice critical thinking and problem-solving in a relaxed, low-pressure environment.
By integrating these strategies consistently, you can help your child build the foundational skills needed for success in both testing and real-world challenges. Here are some practical and engaging approaches to get started:
Encourage your child to work on puzzles or build with blocks to improve spatial reasoning and pattern recognition. Activities like jigsaw puzzles or LEGO construction help them practice visualizing how pieces fit together, mirroring the skills needed for nonverbal test tasks.
Outdoor games involving shapes, sizes, or colors can strengthen visual-spatial thinking. For example, organizing objects by size or arranging natural items like rocks or leaves helps build classification skills similar to those tested on the exam.
Origami and other paper-folding crafts teach spatial transformations, echoing the concepts in paper folding questions. Folding and cutting paper helps children visualize changes in shape and position, enhancing their problem-solving abilities.
Regular exposure to these activities provides a fun and stress-free way to develop nonverbal skills. Consistent practice builds a strong foundation, preparing your child for both the test and future problem-solving challenges.
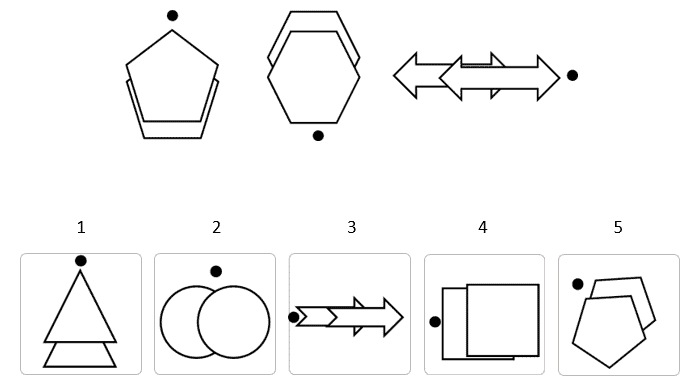
The correct answer is 1.
In this question you can see that:
– All figures consist of three shapes: one black circle and two identical, big, white shapes, when one of them covers part of the other.
– The shape that covers part of the other shape is the shape that is closer to the circle.
In answer choice 1, the shape that covers the other shape is located next to the circle. Therefore, this is the correct answer.
Answer choices 3 and 4 are incorrect because the shape that covers the other is further away from the circle.
Answer choices 2 and 5 are incorrect because both shapes are the same distance from the circle.
Preparing for the nonverbal section requires a focused approach that combines targeted practice, strategic thinking, and activities to enhance visual-spatial reasoning skills.
These elements work together to help your child feel more confident and capable when tackling nonverbal questions. By dedicating time to both structured preparation and engaging, hands-on exercises, you can ensure your child is well-equipped to succeed. Here are some key steps to guide your preparation efforts:
Using practice tests is one of the best ways to prepare. These resources help your child become familiar with the question types, identify patterns, and build problem-solving skills.
Simulating the test environment with timed practice also reduces anxiety and improves focus.
Teach your child to think aloud while solving problems. Verbalizing their thought process helps them understand patterns and relationships.
For figure matrices, guide them to analyze how shapes change and apply that logic to the missing piece. Pattern recognition becomes easier with consistent practice.
Hands-on activities like folding paper, drawing, or assembling puzzles develop visual-spatial reasoning.
These exercises engage the same skills needed for solving tasks like paper folding and shape classification, making them excellent preparation tools.
Developing a growth mindset can greatly enhance your child’s preparation for the nonverbal section. Encourage them to see challenges as opportunities to learn, not as setbacks.
Remind them that mistakes are valuable learning experiences, helping them improve problem-solving skills over time.
Celebrate small achievements, like solving a difficult puzzle or discovering a new pattern. These moments build confidence and motivate continued effort.
Focus on their hard work rather than the outcome. Reinforce the idea that consistent practice and perseverance lead to progress.
Providing emotional support during preparation reduces stress and helps your child approach the test with confidence and a positive attitude, boosting both performance and resilience.
Here are answers to frequently asked questions about the Nonverbal section of the Cognitive Abilities Test.
The Nonverbal section measures visual-spatial reasoning, while the Verbal section evaluates language skills, and the Quantitative section focuses on math-based problem solving.
The Nonverbal section is especially suitable for children who excel at recognizing patterns and shapes without relying on language or numerical skills.
An average Standard Age Score (SAS) is 100, while a score of 115 or higher indicates strong performance. Scores above 130 are often required for admission to gifted programs.
Parents can support their children by using practice tests and encouraging activities like puzzles, drawing, and building projects to enhance spatial reasoning. Consistent practice in a supportive environment improves both skills and confidence.
The Nonverbal section helps identify and develop a child’s visual-spatial reasoning abilities. These skills are vital for excelling in subjects like math, science, and engineering, where recognizing patterns and understanding spatial relationships are essential.
They also support creative fields like design and art by enhancing problem-solving and visualization.
Strengthening nonverbal reasoning builds a foundation for critical thinking, encouraging children to approach problems from different angles. This skill benefits both academic performance and real-world decision-making.
Through practice tests and hands-on activities, children can improve their ability to analyze and solve complex problems.
These efforts not only enhance test performance but also prepare them for long-term success in various academic and STEM fields.
Preparing for the CogAT Nonverbal Battery is an excellent way to strengthen your child’s visual and spatial reasoning skills. These are crucial for academic and real-world success.
You can help your child excel in this section by using practice tests and engaging in hands-on activities like puzzles and origami. Encouraging regular problem-solving exercises further develops the essential skills they need for success.
These skills not only contribute to better performance on the test but also build a foundation for success in subjects like math, science, and engineering. They also foster confidence, enabling children to approach challenges with a positive and determined mindset.
Nonverbal reasoning helps children think critically, recognize patterns, and solve problems more effectively—skills that will serve them well throughout their education and beyond.

Sharpening your child's skills with lifelike practice for gifted tests and school exams.
© 2025 GiftedReady | HTML Sitemap